In the field of engineering and product development, understanding the physical behavior of objects is fundamental. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computer simulation technique used to predict how a product will react to physical forces, vibrations, heat, fluid flow, and other real-world effects.
Unlike manual calculation methods, which can be limited by complex geometries, FEA allows a solid object to be broken down into numerous finite elements to analyze its response in detail. This methodology relies on mathematical models that help understand stress points and potential deformations before proceeding with any phase of physical manufacturing.
Fundamentals of Finite Element Analysis: How does it work?
The concept behind Finite Element Analysis is the subdivision of a continuous body into smaller, more manageable parts. This process is mathematically known as “discretization”.
The mesh structure
When performing a Finite Element Analysis, a network of points called nodes is created, which are connected to form simple geometric elements. The set of these elements and nodes is called a “mesh”. The density of this mesh is crucial: the finer it is in critical areas, the more accurate the analysis results will be.
Equations and numerical solutions
For each element of the mesh, the software applies mathematical equations based on the laws of physics (such as the laws of elasticity or thermodynamics). The system solves thousands of equations simultaneously to determine the displacements at each node. From these displacements, the stresses, and strains throughout the model are calculated.
Applications of Finite Element Analysis in engineering
Finite Element Analysis is a versatile tool applied in various fields of study to evaluate the performance of a design:
– Static analysis: Used to determine stress and displacement levels in structures subjected to constant loads.
– Dynamic analysis: Evaluates how objects respond to loads that change over time, such as vibrations or impacts.
– Heat transfer: Allows for the analysis of temperature distribution and the flow of thermal energy through components.
– Fatigue analysis: Helps predict the service life of a material under repeated loading and unloading cycles, identifying when structural failure might occur due to prolonged use.
Advantages and limitations of FEA
Like any technical tool, Finite Element Analysis (FEA) presents both benefits and important considerations:
– Virtual environment: It allows observation of a design’s behavior under conditions that would be difficult or costly to replicate in a physical laboratory.
– Identification of technical flaws: It helps visually detect areas where the design might be overloaded or where the material could be optimized.
– User dependence: The quality of a Finite Element Analysis depends directly on the initial configuration performed by the analyst. If the boundary conditions or applied loads are unrealistic, the results will also be unrealistic.
– Computational resources: Extremely detailed models require high processing power and considerable computation time.
Frequently asked questions
Not necessarily. Although it reduces the number of prototypes needed, in many industries, final physical testing remains a regulatory requirement to validate the results obtained in virtual simulations.
Metals, plastics, ceramics, composites, and even biological tissues can be analyzed, provided their physical and mechanical properties are known and can be entered into the software.
No. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is used to create the design geometry, while Finite Element Analysis is the tool that subjects that design to virtual physical testing.
Final words
Finite Element Analysis represents a significant advancement in understanding how structures and mechanisms function. Its ability to decompose physical complexity into understandable mathematical data offers profound insights into material behavior and design integrity.
The study and application of this methodology continue to expand as computing power increases, enabling increasingly realistic simulations. Ultimately, knowledge of Finite Element Analysis is a valuable technical skill in modern engineering and scientific development.
We have full confidence in our clients’ ability to overcome any challenge, which is why we offer comprehensive solutions and specialized consulting to support them at every stage on the path to excellence.
Together, we can build the future your business deserves.

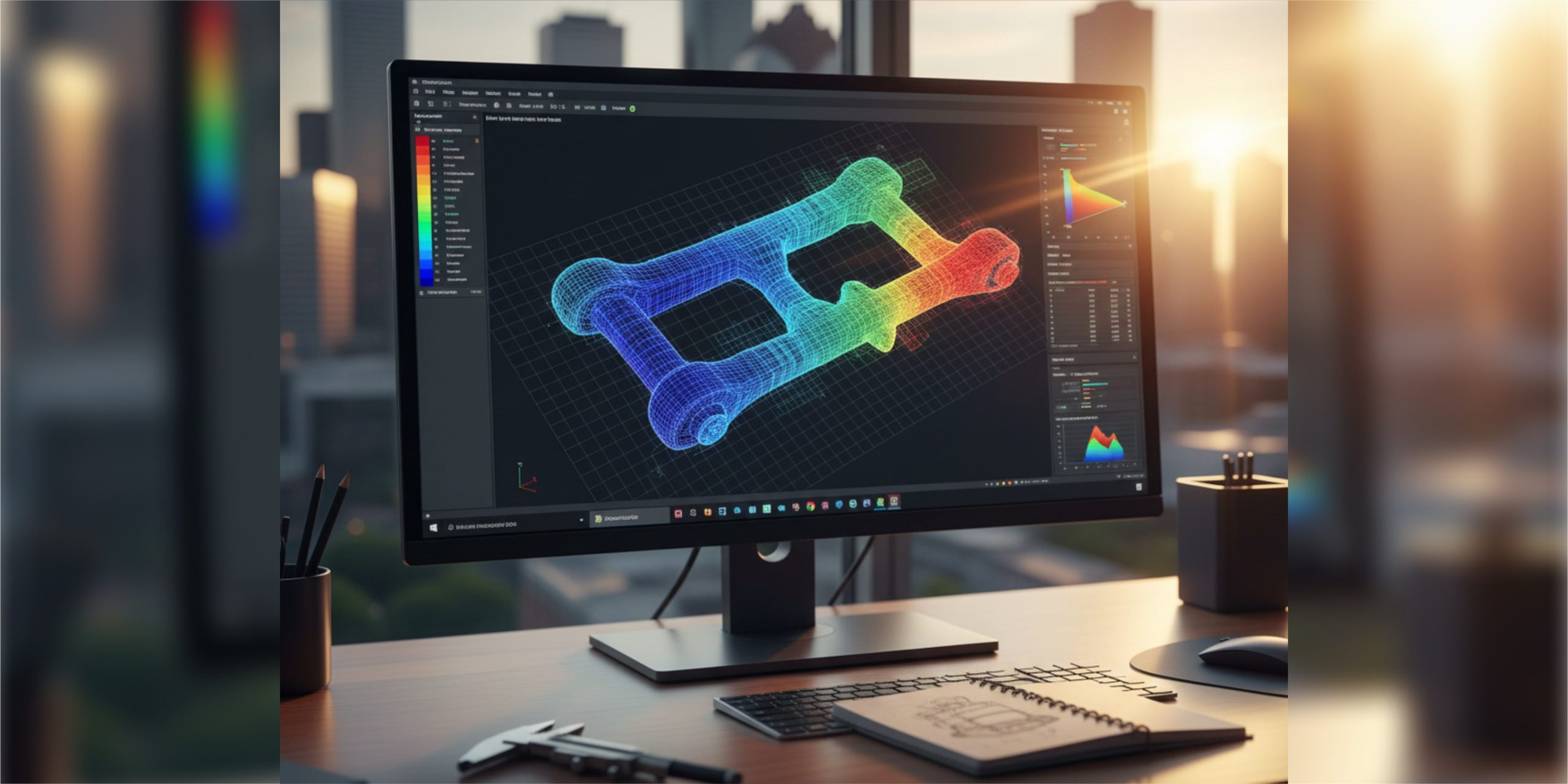



It’s remarkable how technology enables us to identify problems before they occur in real life. Greetings from Houston.
Indeed, the ability to anticipate critical points is what makes this technique invaluable. Thank you very much for your feedback.