In the landscape of modern manufacturing, the choice of cutting technology is a strategic decision that can directly impact the quality, efficiency, and costs of a project. For companies looking to optimize their processes, the comparison between laser cutting and waterjet cutting is a fundamental and ongoing debate.
Although both are advanced and powerful tools, their technical differences make them ideal for very different scenarios.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date guide, offering the necessary information for companies to make informed decisions. It will analyze in detail the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each method, including crucial factors such as precision, speed, compatible materials, and effects on the workpiece. The ultimate goal is to provide clear and practical recommendations that enable professionals to select the most suitable technology for their specific requirements, thereby enhancing the quality of their products and the competitiveness of their operations.
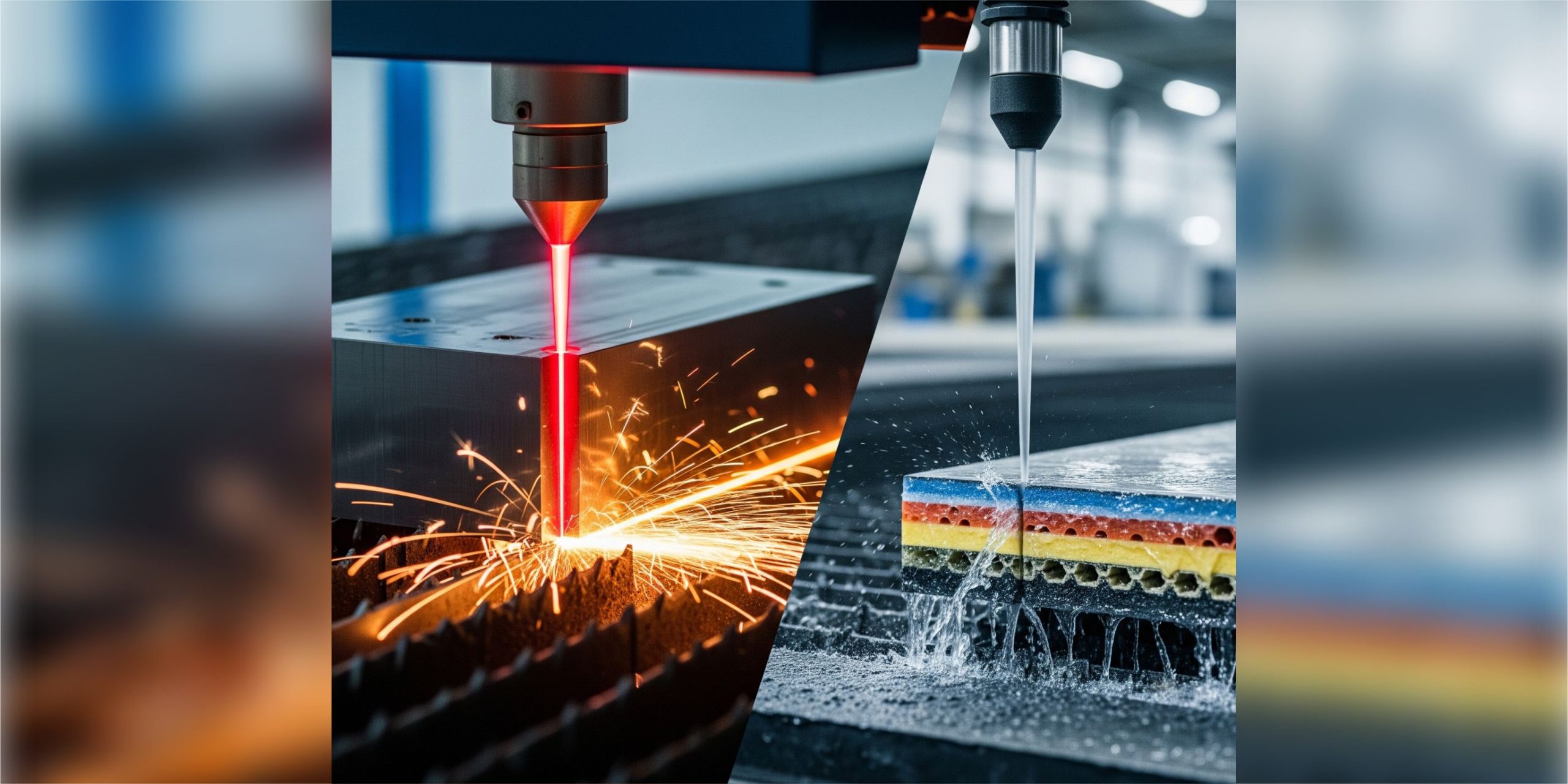
Laser cutting: The technology of concentrated light and heat
Laser cutting is a thermal cutting process that has evolved significantly over the past decades. It uses a highly concentrated and coherent beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize the material at an extremely small focal point.
How does laser cutting technology operate?
The process begins in a resonator, where a high-energy laser beam is generated. This beam is guided through a system of mirrors and lenses that focus it into a nozzle, creating a point of high thermal intensity. When it impacts the material’s surface, the heat energy is so intense that it instantly melts or vaporizes it. An assist gas (such as oxygen for oxidative cuts or nitrogen for clean cuts) is injected at high pressure to blow molten material out of the cut, leaving a clean and precise edge.
The most common machines in 2025 are fiber lasers, which offer superior energy efficiency and a greater ability to cut reflective metals like stainless steel and aluminum, outperforming traditional CO2 lasers in many industrial applications.
Main advantages of laser cutting
– Speed and productivity: For thin and medium-thickness materials (up to 12 mm in steels), laser cutting is incredibly fast. Its high head movement speed and energy efficiency make it ideal for mass production and projects with tight deadlines.
– Precision and finish quality: The focused light beam produces an extremely narrow kerf (cut width), generally below 0.2 mm. This allows for cuts with very tight tolerances and intricate details. The edge quality is smooth, clean, and with minimal burrs, often eliminating the need for additional finishing processes.
– Controlled heat-affected zone (HAZ): Although it is a thermal process, the laser’s HAZ is very small and localized. This minimizes part deformation, making the process well-suited for components requiring high-dimensional accuracy.
– Automation and operational efficiency: Laser cutting systems are highly automatable and easily integrated with CAD/CAM software and CNC control systems, allowing for precise, repeatable operation and continuous production.
Limitations to consider in laser cutting
– Material and thickness restrictions: Laser capability drops drastically with increasing material thickness. Also, it is not ideal for non-metallic materials such as glass, ceramic, or marble, as heat can cause fractures.
– Thermal effects on the material: Despite having a small HAZ, heat can alter the metallurgical properties of the material at the cut edge, causing hardening, brittleness, or even color changes. This is a critical consideration for certain alloys.
– Initial investment cost: High-power laser cutting equipment can require significant initial investment compared to other technologies, although operating costs tend to be lower in the long term.
Waterjet Cutting: The Power of Nature in Industry
Water jet cutting is a cold cutting technology that uses an ultra-high-pressure water jet, often mixed with an abrasive material, to erode the material.
How does water jet technology operate?
The heart of the system is a high-pressure pump that compresses water to levels that can exceed 90,000 PSI. This high-speed water is channeled through a small-diameter nozzle. To cut hard materials, an abrasive (usually garnet) is introduced into the water flow, creating an extremely powerful jet. This jet erodes the material in a controlled manner without generating heat.
Main advantages of water jet cutting
– Material versatility: This is the primary advantage of water jet technology. In the comparison of laser cutting vs. water jet cutting, water jet wins for its ability to cut virtually any material: metals, plastics, glass, composites, ceramics, stone, rubber, and more.
– Absence of heat-affected zone (HAZ): As a cold cutting process, water jet cutting produces no heat. This means material properties remain unchanged, with no deformation, hardening, microcracks, or residual stresses. This is vital for heat-sensitive materials or precision components manufacturing.
– Capability to cut thick materials: Water jet is the preferred technology for cutting thick materials. It can cut steel plates over 20 cm thick, with a cutting capacity significantly greater than any laser.
– Safety and environmental benefits: The process does not produce toxic fumes or hazardous gases, making it safer for operators. Water and abrasive residues can be filtered and, in many cases, recycled, reducing environmental impact.
Limitations to consider in water jet cutting
– Cutting speed: Water jet is generally slower than laser cutting, especially for thin materials. This can be a limiting factor for high-volume production of small parts.
– Precision and finish quality: Although very precise, water jet cutting can exhibit slight tapering on the cut edge, especially in thick materials. The surface finish is good but may be rougher than laser cutting, possibly requiring secondary finishing.
– Operating costs: Water jet operating costs are higher than laser due to abrasive consumption and maintenance of high-pressure pumps and nozzles.
Detailed comparison: Laser cutting and waterjet cutting
To make the best decision, each factor in the comparison between laser cutting and water jet cutting should be analyzed in the context of a specific project.
Speed and productivity
– Laser cutting: Stands out for its high speed on thin and medium-thickness materials. It is the most productive option for the mass production of small metal parts.
– Water jet cutting: Slower on thin materials, but its speed is consistent, and its cutting capacity is unbeatable on thick materials where lasers cannot reach.
Precision and finish quality
– Laser cutting: Offers millimeter-level precision and a superior edge finish that rarely requires post-processing.
– Water jet cutting: Very precise, but the taper phenomenon on thick materials and the possibility of a rougher finish place it one step below laser cutting in this aspect, depending on the project requirements.
Types of materials and thickness
– Laser cutting: Specializes in metals, being very efficient with carbon steel, stainless steel, and certain aluminums. It is not suitable for materials like glass, stone, or thick composites.
– Water jet cutting: Material versatility is its hallmark. The laser cutting vs. waterjet cutting comparison is clear here: waterjet can cut almost anything that fits into the machine, regardless of hardness or reflectivity.
Effects on material and heat-affected zone
– Laser cutting: Heat can generate stresses and alter material properties at the cut edge, which is a risk for parts that cannot tolerate dimensional or structural changes.
– Water jet cutting: Being a cold process, there are no thermal effects. The material retains all its original properties, making it ideal for critical components in industries like aerospace or medical.
Operating and maintenance costs
– Laser cutting: Has low operating costs regarding consumables (gases), but the initial investment can be very high. The maintenance of optics and the resonator requires specialized personnel and is costly.
– Water jet cutting: Initial investment may be lower, but hourly operating costs are higher due to abrasive consumption and maintenance of the high-pressure pump and cutting nozzles.
How to choose the best option? Recommendations for your project
The final decision between laser cutting and water jet cutting should be based on a thorough analysis of your needs and technical requirements.
Choose laser cutting if:
– Your project involves high-volume production of thin to medium-thickness metal parts (up to 12 mm).
– Speed and cycle time are the most critical factors.
– The part requires extreme precision and flawless finish without post-processing.
– The materials you cut are mainly ferrous metals and are not sensitive to minimal thermal effects.
Choose water jet cutting if:
– Your business processes a wide variety of materials, including composites, glass, stone, or plastics.
– The parts are thick or have complex geometries that cannot be cut by a laser.
– Structural integrity of the material is critical, and any thermal alteration is unacceptable.
– The cost of abrasives and cutting time is less critical than material versatility and the absence of heat effects.
Frequently asked questions
Total cost depends on the project. For high-volume production of thin metal parts, laser is usually more economical in the long term. However, for prototypes, small batches, or thick and diverse materials, waterjet may offer a better cost-benefit ratio.
Capability has improved, but highly reflective metals like copper, brass, and pure aluminum remain difficult to cut efficiently with CO2 lasers. Fiber lasers have advanced in this area, but water jet cutting remains the most versatile option for these materials.
Water jet cutting is very clean in terms of absence of fumes and toxic gases. Regarding the finish, it may be slightly rougher than laser cutting, but the lack of thermal effects and ability to cut complex materials often compensate for this difference.
Final words
As we have seen, the choice between laser cutting and water jet cutting is not a matter of superiority but of application. Both technologies represent cutting-edge solutions for modern manufacturing. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses allows companies to make decisions that optimize the quality and profitability of their products.
With a clear focus on innovation and engineering, our team of experts at PBI Solutions is ready to advise your company on the path to excellence. Our mission goes beyond mere technology: we aim to be the strategic partner who helps identify the most efficient solutions, ensuring your vision is realized with the highest precision and quality in the market.
At PBI Solutions, we fully trust our clients’ ability to overcome any challenge. That’s why we provide comprehensive solutions and specialized advice that accompany them at every stage on the road to excellence.
Together, we can build the future your business deserves.





Excellent article. For companies seeking to optimize production speed for thin sheets, lasers remain the most effective solution. Understanding these limitations is crucial to avoid unnecessarily increasing operating costs. Your analysis is very professional.
Dear Ms. Miller, we greatly appreciate your feedback. The speed of laser technology in thin gauges provides a significant competitive advantage. Thank you for valuing our technical analysis.